classification of Animals
| Animals classification |
It is based on where they live(land, water), What They eat, Base on their habitats, body complexity, feeding habits, reproduction, etc. |
| Animals General Classification based on |
Based on backbone (Vertebrates, Invertebrates), Nutrition(Herbivores, Carnivores and Omnivores), Place They Live(Terrestrial Animals, Aquatic Animals, Aerial Animals, Arboreal Animals, Amphibians, Parasites), Decomposers. |
| Species on earth |
Approximately 1.2 million species |
| Animals Characteristics |
Huge Range |
| Example |
Birds(Vertebrates, warm Blooded, 2 legs, Lay eggs, some can fly, have feathers,Breathe with lungs, most live in land and water)Examples : Parrot, duck, peacock e.t.c
Reptiles(Vertebrates, Cold Blooded, Lay eggs, skin is dry,Breathe with lungs, most live in land and water)Examples: Snake, lizard , tortoise, lizard, crocodile e.t.c
Fish(Vertebrates, Cold Blooded, Dont have legs, Lay eggs, Breathe with gills, live in water)Example: Swedish, McFish, Puff Daddy, Floater e.t.c
Mammals(Vertebrates, warm Blooded, Gives birth and feed milk, some can fly, Lay eggs, Breathe with lungs, most live in land and water) Examples: rats, cats, dogs, deer, monkeys, apes, bats, whales, dolphins, and humans.
|
| Habitat |
It depends on where they live / kind places (region land(plains, deserts, mountains) / water (lakes, rivers, and oceans) / both). |
Classification of Animals based on Body Structure
| Animals Classification based on Body Structure |
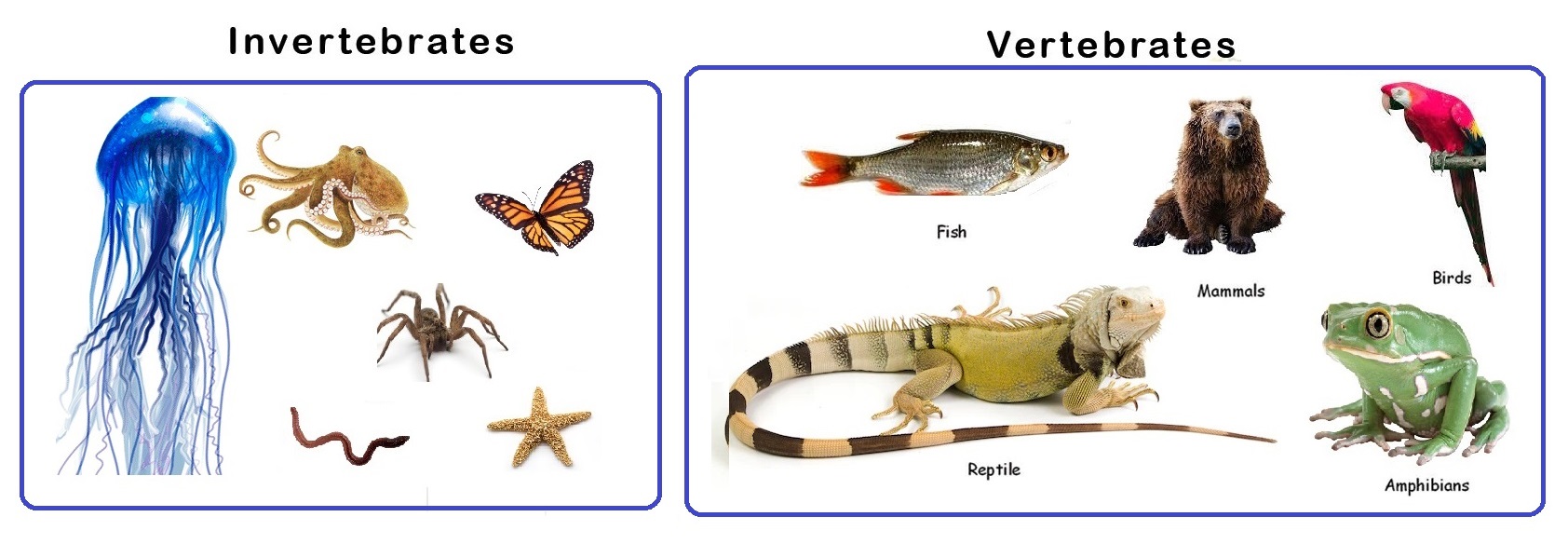
It is based on presence and absence of the vertebral column (backbone). |
| Vertebrates |
Here in Animals, vertebral column (backbone) is Present |
| Invertebrates |
Here in Animals, vertebral column (backbone) is Not Present |
| Invertebrates features |
The animals which dont have vertebral column are called as invertebrates.
It contains a bendy frame consist of head, thorax, and stomach, small in size and reproduce sexually (some) and asexually(others).
|
| Invertebrates Examples |
1. Sponges
2. Unsegmented Worms: Tapeworm, Roundworms, e.t.c.
3. Segmented Worms: Earthworms, Leech, And So On.
4. Arthropods: Cockroaches, Millipede, Centipede, Mosquitoes, Prawns, Crabs, e.t.c.
5. Echinoderms: Starfish, Sea Cucumber, e.t.c.
6. Molluscs: Snails, Oysters, Octopus, e.t.c.
|
Vertebrates
| Vertebrates features |
The animals which have vertebral column are called as vertebrates.
It contains a bendy frame consist of head, thorax, and stomach, small in size and reproduce sexually (some) and asexually(others).
|
| Vertebrates Examples |
birds, mammals, fishes, lampreys, amphibians, and reptiles. E.T.C
|
Classification of Animals primarily based on Nutrition
Classification of Animals primarily based on Nutrition are of 3 types.They were
1. Herbivores / Heterotrophs.
2. Carnivores.
3. Omnivores.
| Classification Based on Nutrition |
Animals whose Primary Food Source |
| Herbivores Definition |
Animals whose primary food source is plant based are called as Herbivores and they cant prepare the food by their own. |
| Carnivores |
Animals whose primary food source is meat / flesh of other animals are called as Carnivores and they cant prepare the food by their own. |
| Omnivores |
Animals whose primary food source is plant based and meat / flesh of other animals are called as Omnivores. |
Herbivores Details
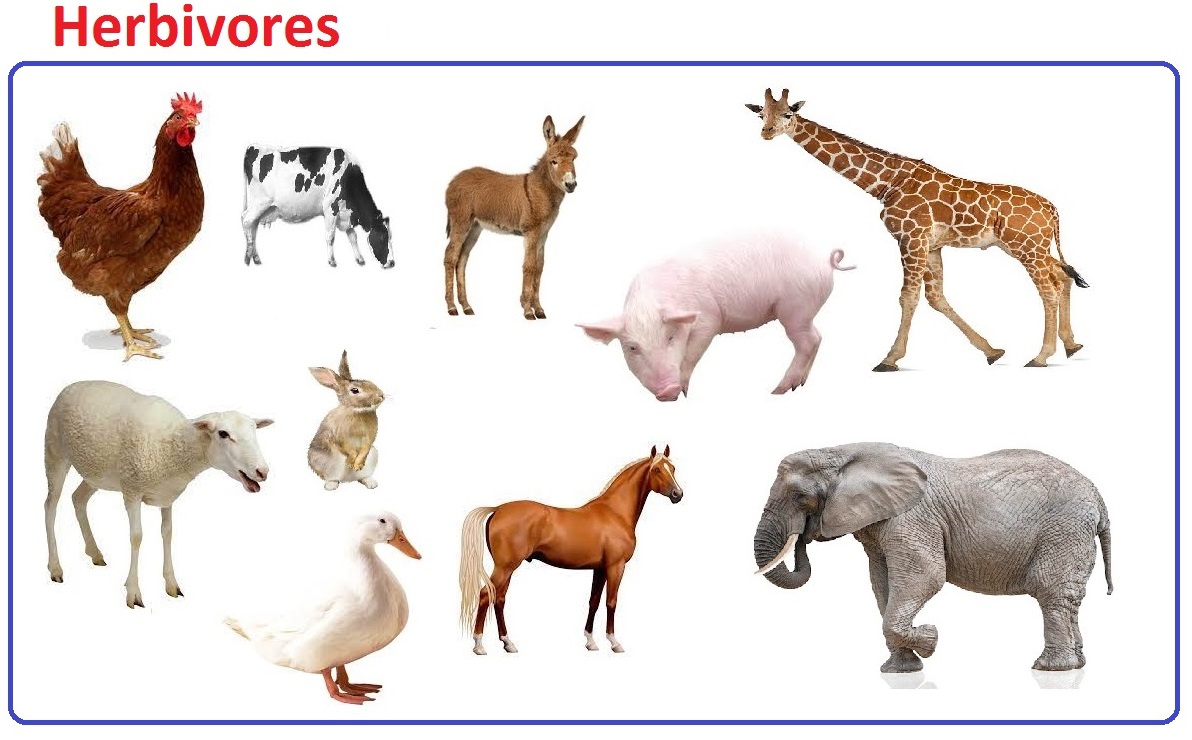
| Herbivores Definition |
Animals whose primary food source is plant based are called as Herbivores and they cant prepare the food by their own. |
| Herbivores Feed |
upon grasses, plant leaves, and other plant products |
| Herbivores Examples |
antelope, beaver, bison, buffalo, camel, cow, deer, donkey e.t.c |
Types of herbivores
| S.No |
Type |
Animals Feed on / consume grain /consume seed / suck / consume leaves |
| 1 |
Frugivores |
Feed on fruits. |
| 2 |
Granivores |
Grain / seed consuming animals. |
| 3 |
Nectivores |
Suck the flower nectar. |
| 4 |
Flavivores |
Consume leaves. |

Carnivores / Meat Eater
| Carnivores Definition |
It is a animal whose primary food source is meat / flesh of other animals. |
| Examples |
Lions, tigers, foxes, eagles, etc. |
| Prey Definition |
The animals that are being killed |
| Predator Definition |
Animals who kills. So carnivores is a Predator. |
| Carnivores capabilities to
seek and seize animals |
Arobust legs to run fastly to capture the prey and sharp claws help to injure the prey. |

Omnivores
Animals whose primary food source is plant based and meat / flesh of other animals are called as Omnivores.
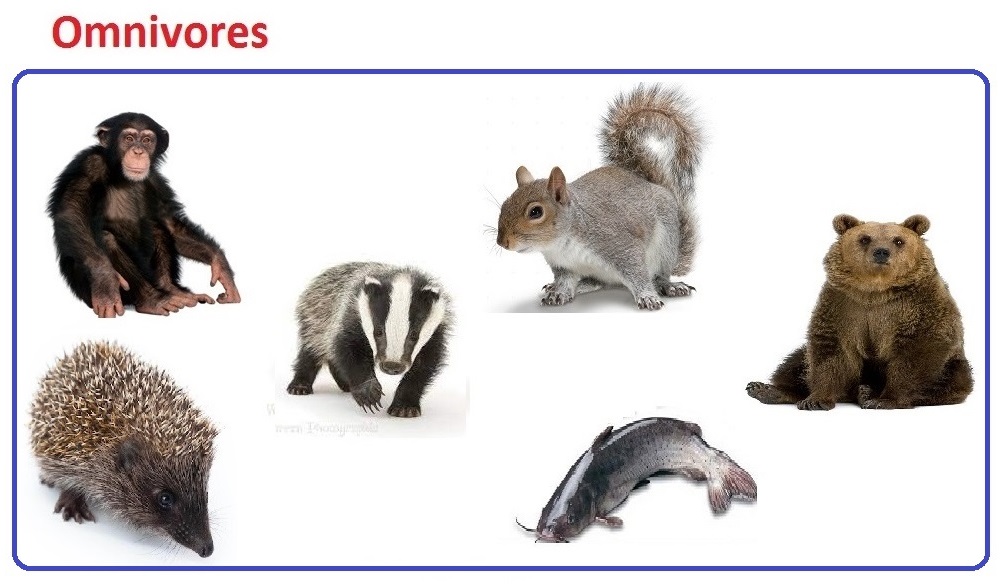
| Omnivores Definition |
Animals whose primary food source is plant based and meat / flesh of other animals are called as Omnivores. |
| Omnivores Examples |
Badgers,Civets, Catfish, Piranhas, Chimpanzees, Squirrels, Hedgehogs, Bonnethead sharks e.t.c |

Terrestrial Animals
| Terrestrial Animals Definition |
The animals that stay at the land are called terrestrial animals |
| Terrestrial Animals Examples |
Cats, Ants, Dogs, Raccoons, Spiders, Kangaroos, Tigers, Lions, Mice, Bats, Bulls, Oxen, Leopards, Elephants E.T.C |
| Terrestrial Animals Features |
Have Skin, limbs (legs), claws, sharp teeth, hunt different animals / may not, protect themselves from their predators |

Aquatic Animals
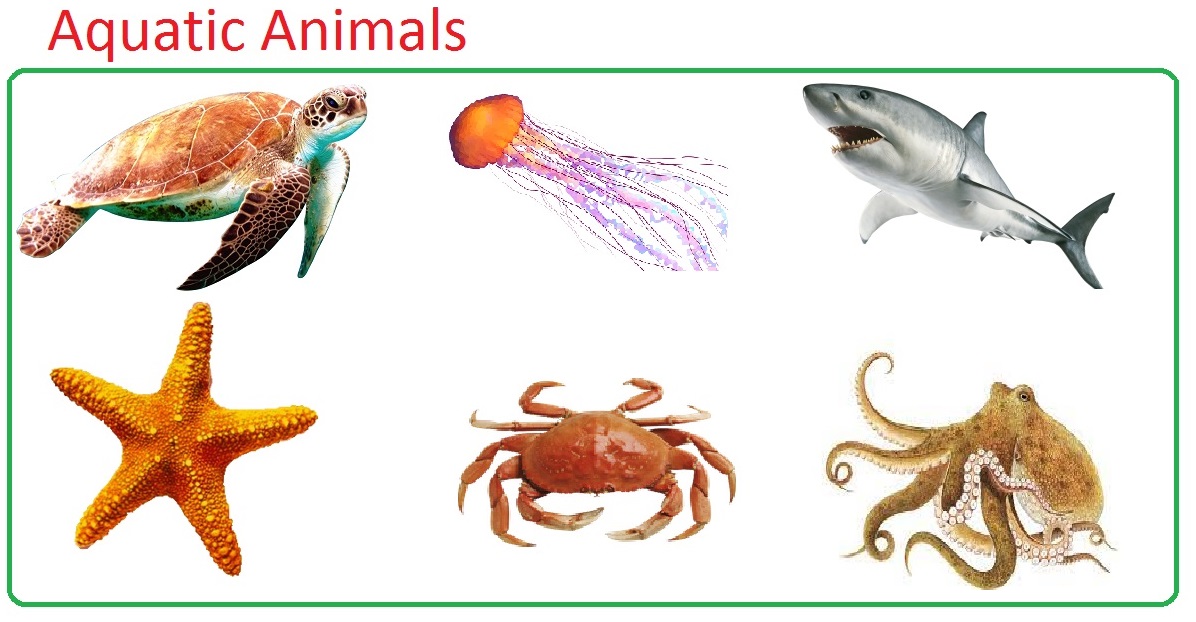
| Aquatic Animals Definition |
The animals that live within the water are called as Aquatic animals. |
| Aquatic Animals Examples |
Fish, Lobsters, Dolphins, Jellyfish, Sharks, Sea Turtles, Starfish, Crabs, Octopus, Whales, Seahorses, Squid, Swordfish, Shrimp, Killer Whales, Manta Rays, Otters, Oysters E.T.C |
| Aquatic Animals Features |
Gills used to breathe underwater, no external ears, swim easily |

Aerial Animals
| Aerial Animals Definition |
The animals which can fly in the air for a numerous time called as Aerial animals. |
| Aerial Animals Examples |
Parrot, Butterflies, Wasps, And Fruit Flies, Kingfisher, Pigeon, Albatross E.T.C |
| Aerial Animals Features |
capability to fly in the air, have (wings, limbs , feathers). |
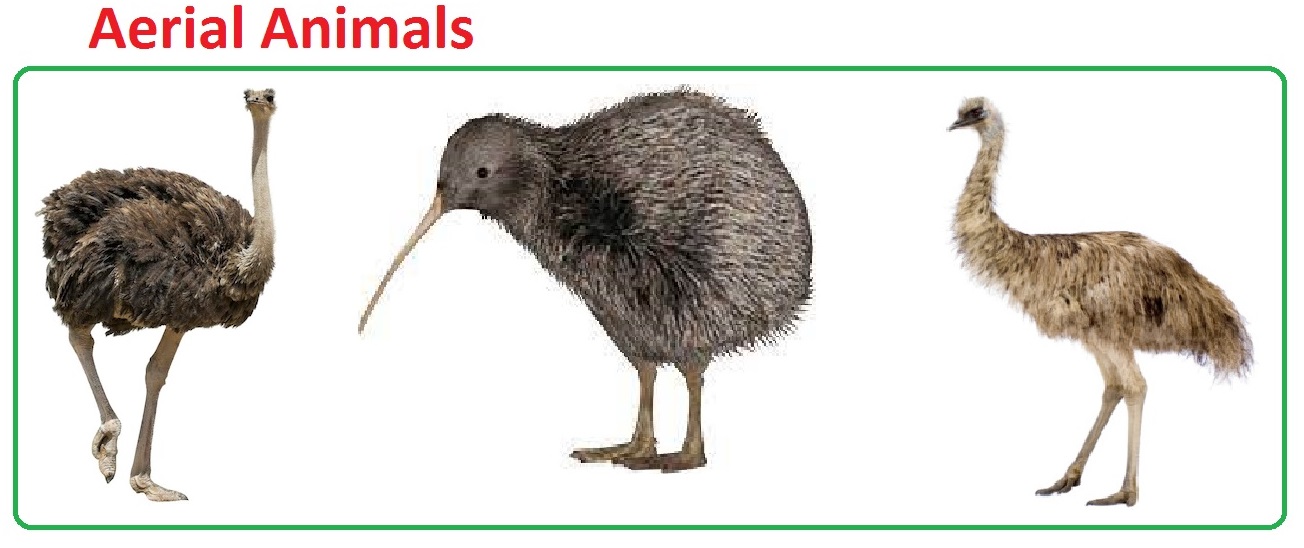
| Aerial Animals Cant Fly |
ostrich, kiwi, emu, e.t.c |

Arboreal Animals
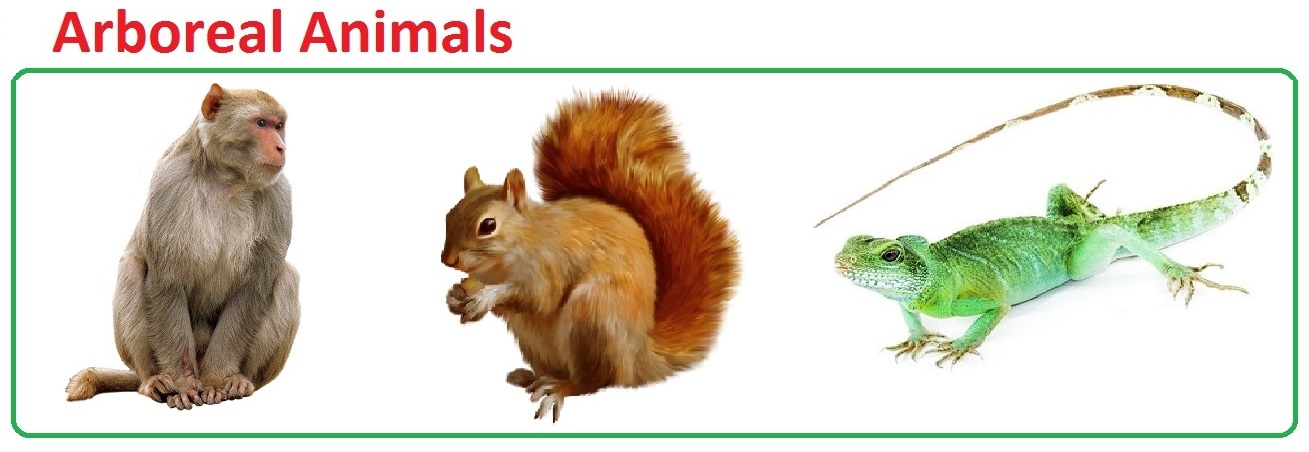
| Arboreal Animals Definition |
These animals which spend most of their time on trees are called as Arboreal Animals. |
| Arboreal Animals Examples |
Monkey, squirrel and tree lizard |
| Arboreal Animals Features |
Have claws and strong legs and arms and climb trees and their branches, swing from one tree to other |

Amphibians
| Amphibians Animals Definition |
These animals which spend their time on water aswell as on land are called as Amphibians Animals. |
| Amphibians Animals Examples |
Frogs, toads, and salamanders |
| Amphibians Animals Features |
forelimbs, finger-like structures, they swim in water, slimy skin, lungs |

Parasites
| Parasites Definition |
It is an organism that lives on / in a host organism and gets food from that host . |
| Parasites Examples |
Protozoa, Helminths, And Ectoparasites |
| Parasites Features |
smaller, depends on host for its food |
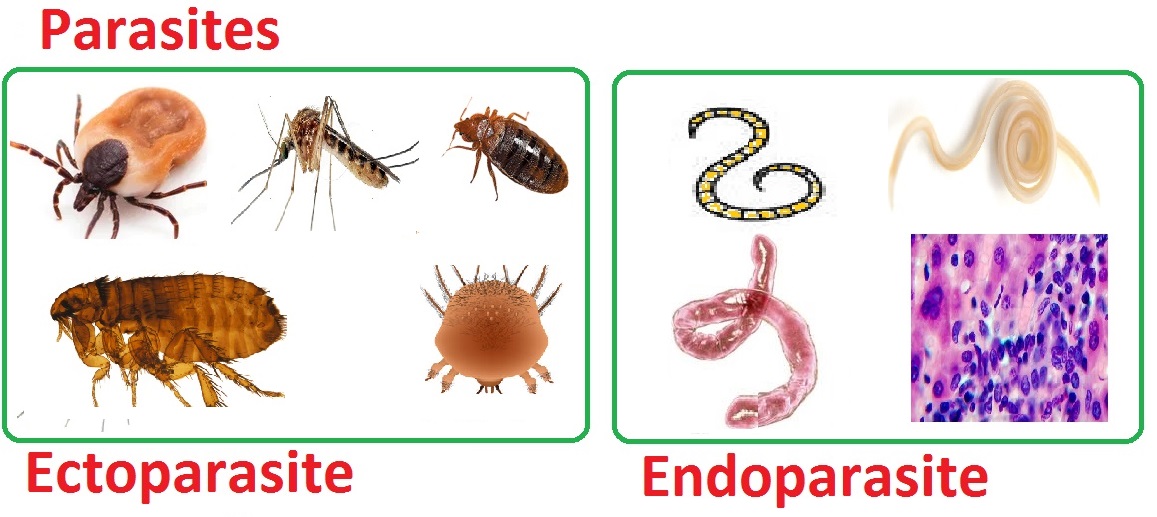
| Types of Parasites |
Ectoparasite and Endoparasite
|
| Ectoparasite |
Ectoparasite are animals Live and gain Nutrition by sucking blood of the host. Example: Mosquitoes, scabies,the common bed bug, fleas and lice etc
|
| Endoparasite |
Endoparasites live inside the host for Nutrition. Example Tapeworms, roundworms,hookworms, ascarids and coccidia |
Scavengers / Decomposers / Environment cleaners
| Scavengers Definition |
Scavengers are animals that consume decaying / dead biomass( meat) |
| Scavengers Examples |
Crows, Vultures, Coyote, Hyena, Jackals, Piranha, Wolves, Ants e.t.c |
| Scavengers Features |
consume the decaying bodies / dead biomass |

|










