|
| Definition | Content Delivery Network is a collection of network of web servers distributed geographically / Points of Presence(PoP). |
| Traditional Method | Storing content on a single central server. |
| Purpose | Faster content delivery. |
| Replication | Data is replicated across all the servers in the internet using CDN. |
| Data Access | User access the data stored closest to him |
| Content Loading Speed | CDN =Fast, Traditional Method = slow. i.e long distance between two objects in communication takes more time. |
| Storing Efficiency | More in CDN compare to Traditional Method. |
| Content Distribution | Done to all geographically distributed data centers |
| Content Delivery Speed | Depends on Location (user is far to server takes more time to retrieve the content otherwise less) |
| Example | Cloud CDN Cedexis by Citrix used by Google |
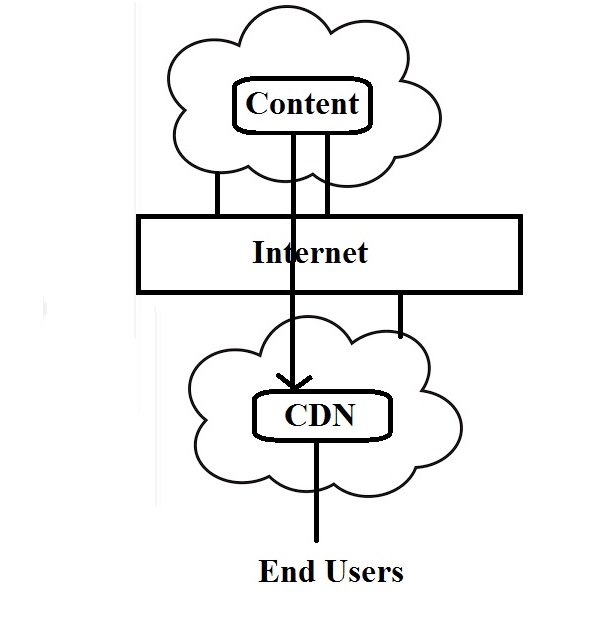
| Content Provider | Organization of Content delivery network. |
| Authorization | It is done by Content Provider to deliver content using CDN. |
| Reporting | CDN provider gives the performance analytics to content provider to evaluate CDN Providerís service quality. |
| Source | Content Provider sends a copy of content |
| Content | It is a digital information created for distribution |
| Request | user requests the Content Provider to view / store data |
| Deliver | CDN delivers the content to user |
| User | User is a entity requests data from the Content Provider. |
CDN architectures key components
| Origin nodes | Data / content is pushed / pulled to origin nodes / servers and stored in Edge nodes for delivery / storage. |
| Control nodes | These are used for management, routing, monitoring and security tools. |
| Delivery nodes | These are used by user are used receive or pull data from storage nodes. |
| Storage nodes | Storage nodes for better latency and lower demand on the origin servers. |
CDN Benefits
| Costs / pricing | For HTTP/HTTP(S), band width are reduced |
| load times | improved |
| global availability of the content | Increased |
| CDN Nodes deployed at | in multiple locations |
| Latency | It is the delay between a user's action and a web application's response. It is reduced. |
Types of content
| Content Type | Details |
| Dynamic content | Web server generates the content by the using programming languages (php, ruby or java). |
| Static content | Content is not generated and dont change. Examples Images, CSS, and JavaScript, etc. |
| Streaming content | These are videos / audio files played using web browser. |
Key features
| For Architects | Global distribution with anycast IP |
| For Developers | Optimized site performance using HTTP/2 and QUIC. |
| For Administrators | CDN is integrated with Stackdriver to provide latency metrics, HTTP request logs for analysis. |
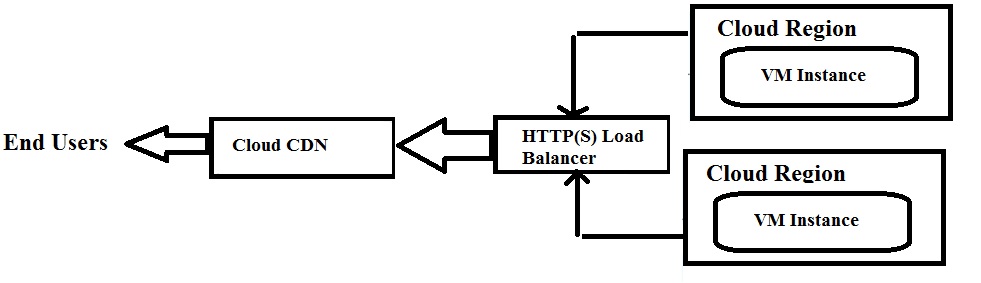
Cloud CDN with HTTP(S) load balancing
Cloud CDN is configured with HTTP(S) load balancer (provides IP addresses and ports numbers for requests) and GKE to deliver content to your users.
Home Back